PLANT MORPHOLOGY
Flower Structure:
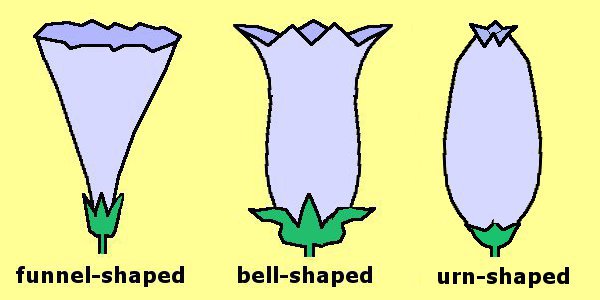
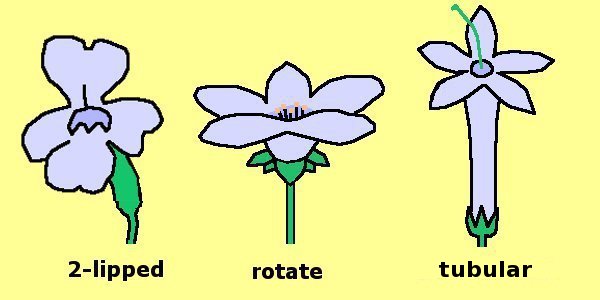
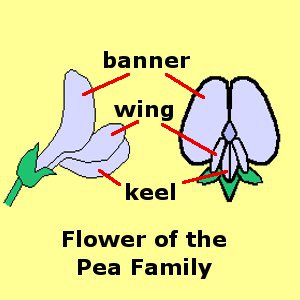
Flower Shape:
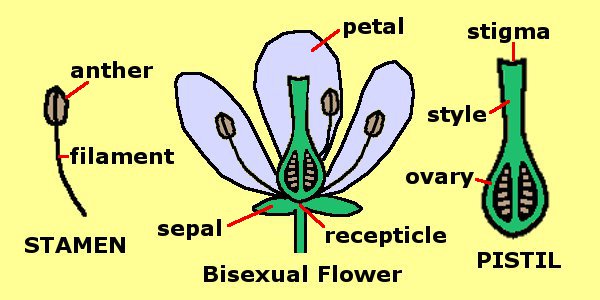
Flower Parts:
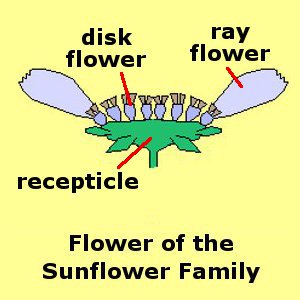
Flower Inflorescence Patterns:

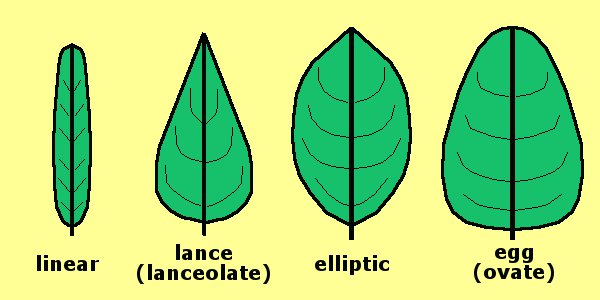
Leaf Structure:
Leaf Shape:

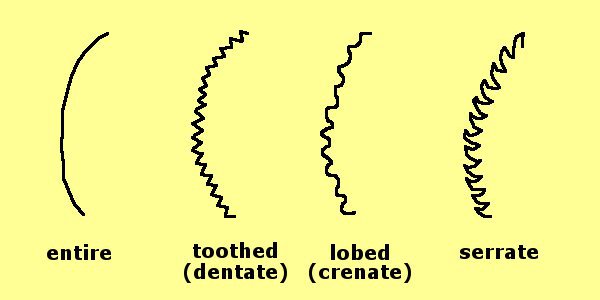
Leaf Margins:
And speaking of leaves, here's a fun little song!
Please send any corrections, questions, or comments to info@blackturtle.us.
|
Commonly Used Terms:
angiosperm - A plant that produces flowers. Two major groups: dicots and
monocots.
annual - A plant that completes its life cycle (germination through
death) in a single year or one growing season. These plants are usually
herbaceous or non-woody.
biennial - A plant that completes its life cycle (germination through
death) in a single year or two growing seasons. In most cases, flowers are
only produced during the second year and plants tend to be herbaceous or
non-woody.
bulb - A short underground stem including the fleshy leaves or leaf
bases attached to it or surround it. For example, an onion.
catkin - A spike or cylindrical cluster of unisexual flowers, with
inconspicuous flowers or flowers producing no petals. For example, willows
(Salix).
caudex - The short, possibly woody, stem of a perennial, located at
or below ground-level.
circumboreal - Found throughout the northern hemisphere, all around
the world.
clone - Individual plants which are genetically identical as a result
of asexual reproduction (budding, fragmentation of rhizomes or stolons,
etc.).
cotyledon - Seed-leaf; the first leaf present when a seed sprouts.
deciduous - Usually refers to plants that are seasonally leafless and
is the opposite of evergreen in this respect.
decumbent - Lying mostly flat on the ground, but with segments
curving upward.
dehiscent - Splitting open upon reaching maturity inorder to release
contents. Often said of seedpods.
dioecious - Staminate and pistillate (male and female) plants
separate, unisexual reproductive structures.
diploid - Having two sets of chromosomes (maternal and paternal).
distal - The far end of something. Farther away from the origin, more
toward the tip or edge.
endemic - Native to a well defined geographical area and restricted
to that area.
ephemeral - Lasting only a short time. Often said of desert herbs,
which complete life cycle in a short period of time.
exserted - Protruding out of surrounding structures. Often describes
the stamens of certain plants.
gymnosperm - Woody plant bearing cones (or in some cases naked on
branches).
habit - General shape or form of a plant. It's characteristic mode of
growth.
haploid - Having one set of chromosomes (either maternal or
paternal). This is the normal state of spores, sperm, and eggs.
herb - A plant with little or no wood above ground. May be annual,
biennial, or perennial.
hispid - Covered with bristly, stiff hairs, rough to the touch.
included - Not protruding out of surrounding structure(s).
intergrade - The gradual merging from one extreme to another through
a series of intermediaries.
internode - The space on the stem between leaves.
interrupted - Having parts spaced unevenly.
involcre - A group of bracts formed more or less as a single
unit.
lenticel - A pore (or spongy area) most commonly found on the
surfaces of twigs or fruits.
margin - The edge of a leaf (or sometimes perianth part).
monoecious - Staminate and pistallate (male and female) structures
found on the same plant.
naturalized - A non-native plant (alien) which inhabits an area
without further human assistance.
pedicel - The stalk of a single individual flower or fruit.
peduncle - The stalk of an entire inflorescence (or of a single
flower or fruit if not part of an inflorescence).
perennial - A plant living more than two years or growing seasons.
polypoid - Having three or more sets of chromosomes (denoted as 3n,
4n, etc.).
proximal - The close end of something. Closer to the origin, farther
away from the tip or edge.
puberulent - Having hairs that are not readily visible without
magnification.
rhizome - An elongated, horizontal, underground stem.
rosette - A radiating cluster of leaves normally at or near ground
level.
saprophyte - A plant usually lacking chlorophyll that lives on dead
organic matter.
scabrous - Rough to the touch normally as a result of having short
stiff hairs.
scapose - Describes a plant or inflorescence with a relatively long
peduncle that arises from the ground, often from a rosette, sometimes
bearing bracts, but leafless.
scarious - Thin, dry, pliable, dark-colored or translucent, but not
green. (For instance, dry onion peel.)
serpentine - General term used to describe rock and soil with exceptionally
high concentrations of magnesium and iron. Characterized by low levels of
calcium and other nutrients and high levels of magnesium, iron, and certain
toxic metals. Many types of plants either require or cannot tolerate this
type of soil.
sessile - Having no petiole, peduncle, pedicel, or other kind of
stalk.
stellate - Like a star. Usually refers to a hair with three or more
branches which radiate out from a common point.
stolon - Normally a thin, elongated stem lying more or less flat on
the ground and forming roots as well as shoots or stems which become
new plants. Also known as a runner.
subshrub - A plant with woody lower stems and upper stems and twigs
which are not woody and which dies back seasonally.
suture - Groove or line of dehiscence or fusion.
tomentose - Covered with dense, interwoven, matted hairs.
unisexual - Plants which produce flowers that have either stamens or
pistils, but not both, which are fertile.
waif - A non-native plant which will not naturalize, but which may
persist in an area for a generation or two before dying away.
|








